You
can create a polar or rectangular array of an object. Arrays of
objects are not created using a dedicated set of functions, but
are created through a combination of copying objects, and then using
a transformation matrix to rotate and move the copied object. The
following outlines the basic logic for each type of array:
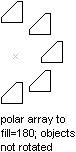
- Polar array.
Copy the object to be arrayed and move it based on an angle around
a the base point. The distance from the object to the base point
of the array is used to calculate the placement of each copy that
is created. Once the copied object is moved, you can then rotate
the object based on its angle from the base point. Once each copy
is created, it needs to be appended to the block table record.
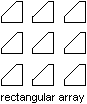
- Rectangular array.
Copy the object to array based on the number of desired rows and
columns. The distance that the copied objects are copied is based
on a specified distance between the rows and columns. You first want
to create the number of copies of the original to complete the first row
or column. Once the first row or column is created, you can then
create the number of objects for the remaining rows or columns based
on the first row or column you created. Once each copy is created,
it needs to be appended to the block table record.
For more information
about arrays, see “Create an Array of Objects” in
the AutoCAD User's Guide.